Cirrhosis is a serious condition that affects the liver and can have a range of symptoms, including muscle wasting. Muscle wasting, or sarcopenia, is a common complication of liver cirrhosis that can lead to decreased mobility and quality of life. The link between cirrhosis and sarcopenia is not well understood, but recent research has shed light on the connection between the two conditions. In this post, we will explore what sarcopenia is, how it is related to cirrhosis, and what you can do to prevent and treat it. Whether you are living with cirrhosis or are caring for someone who is, this post will provide you with valuable information to help you understand and manage the condition.
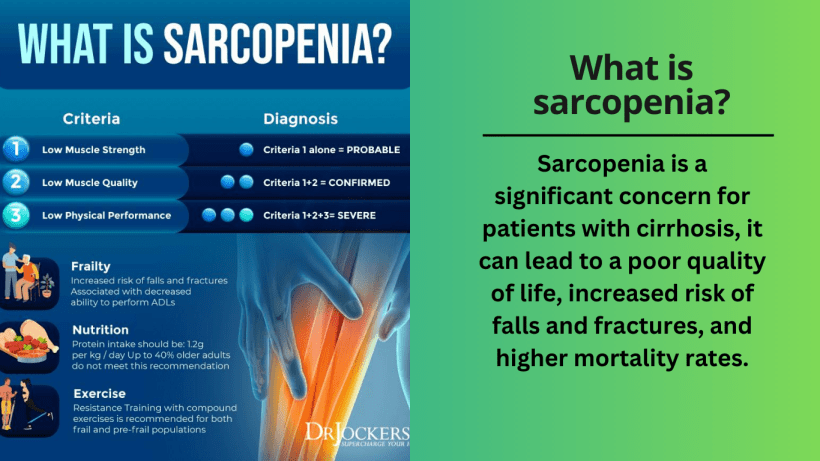
What is Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is a medical condition that refers to the loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, which is commonly associated with cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease that occurs when the liver is damaged and replaced by scar tissue. The liver plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and metabolism, which are essential processes for maintaining muscle mass and function.
When the liver is damaged, it can no longer perform these functions effectively, leading to a decrease in muscle mass and strength. This can result in weakness, fatigue, and reduced physical activity, which can further exacerbate the condition.
Sarcopenia is a significant concern for patients with cirrhosis, as it can lead to a poor quality of life, increased risk of falls and fractures, and higher mortality rates. Therefore, early detection and management of sarcopenia are crucial in improving outcomes for patients with cirrhosis.
Several interventions can help prevent or manage sarcopenia, such as exercise, nutritional support, and medications. However, these interventions should be tailored to the individual needs of the patient and should be supervised by a healthcare professional. By understanding sarcopenia and its link to cirrhosis, patients and healthcare providers can work together to improve outcomes and maintain muscle health.
Common causes of sarcopenia
One of the most common causes of sarcopenia is malnutrition. Malnutrition is a common problem in cirrhotic patients due to the reduced intake of nutrients and the reduced ability of the liver to store and metabolize nutrients. This can lead to a deficiency in essential nutrients such as protein, vitamins, and minerals, which are essential for muscle growth and maintenance.
Another common cause of sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients is physical inactivity. Patients with cirrhosis often experience fatigue and weakness, which can lead to a sedentary lifestyle and reduced physical activity. This lack of physical activity can cause the muscles to weaken and waste away, leading to sarcopenia.
Other factors that can contribute to the development of sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients include hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These factors can disrupt the normal processes involved in muscle growth and maintenance, leading to the loss of muscle mass and strength.
In order to prevent and manage sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients, it is important to address the underlying causes of the condition. This may involve interventions such as nutritional support, exercise programs, and medication to manage hormonal imbalances and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. By addressing these factors, it is possible to slow or even reverse the loss of muscle mass and strength in patients with cirrhosis.

How sarcopenia is diagnosed
The diagnosis of sarcopenia involves a comprehensive examination, medical history review, and specific tests. The medical professional will take a history of the patient’s symptoms, such as muscle weakness, weight loss, and physical limitations. They will also conduct a physical examination to assess muscle mass, strength, and function.
Tests will be conducted to measure the muscle mass, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Blood tests will also be done to check for any underlying conditions that may be contributing to muscle loss, such as liver function tests, kidney function tests, and thyroid function tests.
If sarcopenia is suspected, additional tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered to assess the severity of the muscle loss and identify any underlying causes.
It’s important to note that early detection and diagnosis of sarcopenia is crucial for the optimal management of the condition. Therefore, it’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have symptoms of sarcopenia.

What are the symptoms of sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is a condition that can be difficult to diagnose as the symptoms can be similar to those of other diseases. However, there are some key symptoms that are often present in patients with sarcopenia.
One of the most common symptoms of sarcopenia is muscle weakness. Patients may find that they struggle to perform tasks that they would normally be able to do with ease, such as lifting objects or climbing stairs. This weakness can also lead to a general feeling of fatigue and lethargy, which can impact the patient’s quality of life.
Another symptom of sarcopenia is muscle wasting or atrophy. This is where the muscles in the body begin to shrink and become weaker over time. Patients may notice that their clothes are fitting more loosely or that they are losing weight, despite not trying to do so.
In some cases, patients with sarcopenia may also experience pain and discomfort in the muscles. This can be due to inflammation or damage to the muscle tissue.
Other symptoms of sarcopenia may include difficulty walking, poor balance, and an increased risk of falls. Patients may also experience a loss of appetite and a decrease in overall mobility.
It’s important to note that not all patients with sarcopenia will experience these symptoms, and some may only have mild symptoms. If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, it’s important to speak to your doctor as soon as possible to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
The link between liver disease and muscle wasting
Liver disease and muscle wasting are closely linked. When the liver doesn’t function properly, it can lead to a condition known as cirrhosis, which causes muscle wasting. Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease that results in the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, which disrupts the liver’s normal function.
As cirrhosis progresses, the liver’s ability to produce proteins, process nutrients, and regulate hormones is impaired. This can lead to malnutrition, hormonal imbalances, and muscle weakness. Additionally, the buildup of toxins in the bloodstream due to liver damage can further exacerbate muscle wasting.
Muscle wasting in cirrhosis is typically characterized by a loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength. This can lead to decreased mobility, poor quality of life, and an increased risk of falls and fractures. It is important for individuals with cirrhosis to maintain a healthy diet and engage in physical activity to help prevent and manage muscle wasting.
Effective treatment of cirrhosis and its associated complications can also help to alleviate muscle wasting. This may involve medications to manage symptoms, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, liver transplantation. Understanding the link between liver disease and muscle wasting is crucial for effective management of cirrhosis and improving the overall health and well-being of those affected.

The effects of cirrhosis on muscle mass and function
As cirrhosis replaces healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, it starts to affect many vital organs and systems, including nutrition, muscle mass, and muscle function. It is common for patients with cirrhosis to experience muscle wasting, which can significantly impact their quality of life. It is a common complication of cirrhosis, affecting up to 70% of patients with advanced liver disease. The exact mechanisms that cause sarcopenia in cirrhosis are not fully understood, but it is believed that a combination of factors contribute to the muscle wasting, including inflammation, oxidative stress, hormonal imbalances, and physical inactivity.
To prevent and treat sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis, a multidisciplinary approach is required, including nutritional support, physical activity, and medical management of the underlying liver disease. Nutritional interventions should focus on increasing protein and caloric intake, while physical activity should be tailored to the patient’s individual needs and capabilities. Medical management may include medications to improve liver function and reduce inflammation, as well as hormone replacement therapy to restore hormonal imbalances.
Nutritional deficiencies are common in patients with cirrhosis and those who develop sarcopenia. This is because the liver plays an important role in metabolism and the processing of nutrients. When the liver is damaged, as is the case in cirrhosis, it can no longer perform these functions effectively. This can lead to muscle wasting and other complications. Patients with cirrhosis are at risk of developing deficiencies in specific nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals.
To prevent nutritional deficiencies in patients with cirrhosis, it is important to monitor their nutritional status regularly and provide them with adequate nutrition and supplements as needed. This may involve working with a dietitian or nutritionist to develop a customized diet plan that meets the patient’s individual needs and preferences.

Treating and managing sarcopenia
Treating and managing sarcopenia in cirrhosis is a multifaceted approach that requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and therapies.
One of the most effective ways to manage sarcopenia is through exercise. Resistance training, in particular, has been found to be effective in increasing muscle mass and strength in patients with cirrhosis. A study published in the Journal of Hepatology found that progressive resistance training was associated with significant improvements in muscle mass and strength in cirrhotic patients with sarcopenia.
In addition to exercise, nutritional therapy is also an essential component of sarcopenia management. Adequate protein intake is necessary for muscle maintenance, and patients with cirrhosis are often at risk of malnutrition. A diet rich in protein and other essential nutrients can help prevent muscle loss and promote muscle growth.
Medications such as anabolic steroids, growth hormone, and testosterone have also been used to help manage sarcopenia in cirrhotic patients. However, the use of these medications should be carefully monitored due to potential side effects.
Close monitoring of liver function and disease progression is essential in the management of sarcopenia in cirrhosis. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify any changes in liver function and allow for early intervention if necessary.
Knowledge is key
Finally, it’s important for those with cirrhosis to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their condition and address any complications as they arise. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help to identify and address any issues before they become more serious. With proper management and care, it’s possible to prevent or slow down the progression of sarcopenia and other complications of cirrhosis.
I hope this article has helped to shed some light on the relationship between muscle wasting and cirrhosis. sarcopenia is a real concern for many individuals with cirrhosis, and it’s important to understand the underlying mechanisms of this condition. We encourage those who are struggling with muscle wasting to speak with their healthcare provider and consider implementing the lifestyle changes and treatments that we have discussed. We wish you all the best in your health journey and hope to provide more useful insights and tips in the future.

